Ms-5 Dec 2009
MS-5 Dec, 2009
MS-5 : MANAGEMENT OF MACHINES AND MATERIALS
1(a) Explain with the help of a suitable diagram the framework of organising and control in a production system.
(b) On the basis of material flow classify production systems and give examples for each type.
2(a) List down different phases of value engineering approach as used for a product design.
(b) What layout design procedure would you adopt to develop a layout for any small toy unit manufacturing plastic toys at the rate of 5000/day ? Discuss.
3.(a) Why is facility location important ? Discuss different factors important for locating any bread manufacturing unit. Make relevant assumptions.
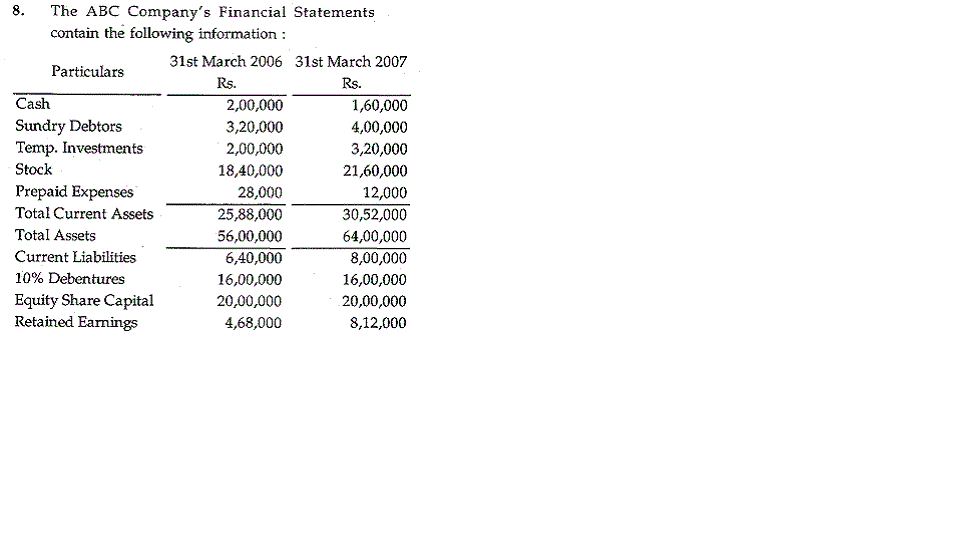
(b) Describe the commonly used control charts for variables and attributes in SQC.
4(a) Discuss in brief various environmental factors taken into consideration for job design.
(b) Discuss objectives of maintenance management. List different types of maintenance system prevalent in manufacturing companies.
5. (a) Consider a situation of; production of a simple product with continuous demand.
The setup cost per batch of size Q is given. Unit variable cost of productions is also known. Derive the equation for optimum batch size. Assume and list major parameters.
(b) Why is mass production preferred over in some types of products with large volume ?
Explain the key elements of mass production with some examples.
6. (a) Explain the major scheduling rules for job shops as being practiced in industry.
(b) Draw CPM network for the following :
Activates Duration (days)
1 - 2 5
1 - 3 3
1 - 4 3
2 - 3 7
4 - 5 6
3 - 4 8
Determine Critical Path.
7. (a) Discuss ABC system of inventory management with examples.
(b) Explain the importance of store location and layout.
8. Write short note on any two of the following :
a) Productivity and waste
b) Value engineering
(c) Materials Requirement Planning
(d) Control charts for variables.
Ms-5 Dec 2010
Ms-5 Dec 2010 solved paper from ignou university you can buy this ms-5 book from this site
Ms-5 Dec 2011
MS-5 Dec, 2011
MS-5 : MANAGEMENT OF MACHINES AND MATERIALS
1. (a) Discuss conceptual model of an operations system. Explain some of the performance objectives in operations management.
(b) Explain the frame work of organising and control in a production system.
2. (a) What are different types of process forms in manufacturing system which are used to effect transformation of inputs into outputs ? Explain with examples.
(b) Choose a major facility of any organization ( manufacturing) and develop a detailed
layout for the same.
3. (a) What are the different types of material handling equipment used in large industries ? What type of material handling system would you recommend for a cement plant.
(b) Discuss advantages and disadvantages of "codification and 'Standardization' of
material." Use examples.
4. (a) Discuss purchase procedure with the help of a schematic diagram.
(b) Explain common approaches for price determination.
5. (a) Discuss systems of vendors evaluation and rating. Also give its importance.
(b) List different steps of value engineering approach, used as a product design tool.
6. (a) Explain operating characteristic curve. With the help of the 0.0 curve explain simple sampling plan.
(b) Discuss objectives of maintenance management. List different types of maintenance systems prevalent in manufacturing organisations.
7. . (a) List some of the major line Balancing methods. Explain any one of the method.
(b) What do you understand by scheduling ? Discuss various dispatching rules as used
in Industry
8. Write short note on any two of the following :
(a) Materials Requirement Planning
(b) Economic order Quantity
(c) Critical Path Method
(d) Job Design
MS-4 june-2007
MS-4 - june-2007
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
1. (a) Explain the Continuity concept and the Periodicity concept and discuss their significance.
(b) Explain the nature of accounting function and describe the role played by the Accountant in a business organisation.
2. The following items appear on the Trial Balance prepared from the books of Mr. Kamal Saxena as on 31st March 2006 after making necessary adjustments for depreciation on fixed assets, outstanding and accrued items and placing the difference under Suspense Account.
Machinery: 1,70,000
Furniture: 49,500
Sundry Debtors: 38,000
Drawings: 28,000
Travelling Expenses: 6,500
Insurance: 1,500
Audit Fees: 1,000
Salaries: 49,000
Rent: 5,000
Cash in hand: 7,800
Cash at Bank: 18,500
Stock in trade (1-4-2005): 80,000
Prepaid Insurance: 250
Miscellaneous expenses: 21,200
Suspense A/c (Dr.): 39,400
Sundry Creditors: 82,000
Capital Account: 2,45,750
Outstanding Expenses :
Salaries: 1,500
Printing: 600
Audit Fees: 1,000
Bank Interest (Cr.): 1,200
Discounts (Cr.): 1,800
Sales less Refurns): 6,80,00
Discount allowed: 1,200
Printing and Stationery: 1,500
Purchases (less Returns): 4,60,00
Depreciation :
Machinery: 30,000
Furniture: 5,500
On a subsequent scrutiny the following mistakes were noticed
(i) A new machinery was purchased for Rs. 50,000 but the amount was wrongly posted to Furniture Account as Rs. 5,000.
(ii) Cash received from Debtors Rs. 5,600 was omitted to be posted in the ledger.
(iii) Goods worth Rs. s,000 withdrawn by the proprietor for personal use, but no entry was passed.
You are further told that :
(a) Closing Stock amounted to Rs. 47,500.
(b) Depreciation on Machinery and Furniture has been provided @ 15% and 10% respectively On declining balance system. Full year's depreciation is provided on addition.
You are required to prepare a Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended on 31st March 2006 and a Balance Sheet as on that date.
3. (a) Explain the concept of cost of capital as a device for establishing a cut-off point for capital investment proposals.
(b) Discuss the limiting factors in the reliability of capital budgeting techniques including the discounted cash flow techniques.
4. (a) What is optimum cash balance ? How can it be determined ? Explain.
(b) Distinguish between Cash Flow Statement and Funds Flow Statement." What purposes do they serve? How do you calculate Funds from Business Operations while preparing a Funds Flow Statement? Explain.
5. (a) Explain the three important control ratios that are used to compare the actual performance with the budgeted performance.
(b) Distinguish between Fixed Budget and Flexible Budget. When is a Flexible Budget considered desirable ? Explain.
6. A company produces a single product which is sold by it presently in the domestic market at Rs. 75 per unit. The present production and sales is 40,000 units per month representing 50% of the available capacity. The cost data of the product are as under:
Variable cost per unit Rs. 50.
Fixed cost per month Rs. 10 lakh.
To improve profitability, the management has 3 proposals on hand as under :
(a) To accept an export supply order For 30,000 units per Month at a reduced price of Rs. 60 per unit, incurring additional variable costs of Rs. 5 per unit towards export packing, duties etc.
(b) To increase the domestic market sales by selling to a domestic chain store 30,000 units at Rs. 55 per unit, retaining the existing sales at the existing price.
(c) To reduce the selling price for the increased domestic sales as advised by the sales department as under :
|
Reduce Selling price |
Increase in Sales |
|
5 |
10,000 |
|
8 |
30,000 |
|
11 |
35,000 |
Prepare a table to present the results of the above proposals and give your comments and advice on the proposals.
7. Comment on the following statements :
(a) Operating cycle plays a decisive role in influencing the working capital needs.
(b) "Debt is a double-edged knife."
(c) Break -even analysis is not without limitations.
(d) Higher profit margin need not necessarily lead to higher rate of return on investment.
(e) A company's profitability is better judged by PBIT rather than by PAT.
8. Write short notes on the following :
(a) Absorption Costing
(b) Zero based Budgeting
(c) Direct Labour Variances
(d) Sunk Costs and Imputed Costs
MS-4 june-2008
MS-4 - june-2008
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
l. (a) What do you understand by the concept of conservatism ? Why is it also called the concept of prudence ? Why is it not applied as strongly today as it used to be in the Past ?
(b) What is a Balance Sheet ? How does a Funds Flow Statement differ from a Balance Sheet ? Enumerate the items which are usually shown in a Balance Sheet and a Funds Flow Statement'
2. (a) Why does depreciation need to be provided on fixed assets and what are the usual methods of providing depreciation
(b) Discuss the role of the Board of Directors in dividend decision
3. What do you understand by Discounted Cash Flow Techniques of Capital Budgeting ? Briefly explain the Net Present Value Method and Internal Rate of Return Method. which of the two would you rank better and why ?
4. Distinguish between :
(a) Financial Leverage and operating Leverage
(b) Cash Budget and Cash Flow Statement
c) FIFO AND LIFO
(d) Preference shares and Rights shares
A company manufactures a single product in its factory utilising 60% of its capacity. The details are given below :
Rs
Sales (6,000 units) 540000
Direct materials 96000
Direct labour 120000
Direct expenses 18000
Fixed overheads :
Factory 200000
Administration 21000
Selling and Distribution 25000
12.5 % of factory overheads and 20% of selling and distribution overheads are variable with production and sales. Administrative overheads are wholly fixed. Since the existing product could not achieve budgeted level for two consecutive years, the Company decides to introduce a new product with marginal investment but largely using the existing plant and machinery.
The cost estimates of the new product are as follows :
Cost elements Rs. per unit
Direct materials 16
Direct labour 15
Direct expenses 1.5
Variable factory overheads 2.0
Variable selling and distribution overheads 1.50
It is expected that 2,000 units of the new product can be sold at a price of Rs. 60 per unit. The fixed factory overheads are expected to increase by t}o/o, while fixed
selling and distribution expenses will go up by Rs. 12,500 annually. Administrative overheads remain unchanged.
However, there will be an increase of working capital to the extent of Rs. 75,000, which would take the total cost of the project to Rs. 8.75 lakh
The company considers that 20% pre-tax and interest return on investment is the minimum acceptable to justify any new investment.
You are required to
(a) Decide whether the new product be introduced.
(b) Make any further observations /recommendations
about profitability of the company on the basis of
the above data after making assumption that the present investment is Rs. 8 lakh.
6- Explain fully the following statements :
(a) "Lower the Break-even point, better it is
(b) "Greater the variability of cash flows, higher should be the minimum cash balance
(c) "Weighted average cost of capital would always be higher, if the market value weights are used. "
(d) "Capitalisation of reserves is different from capital resgrves. "
7 Why do you understand by the term 'pay-out ratio' ? What factors are taken into consideration while determining pay-out ratio ? should a company follow a fixed pay-out ratio policy ? Discuss fully.
MS-4 june-2009
MS-4 - june-2009
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
1. 'Management Accounting is an extension of financial Accounting'. Explain how is Management Accounting..an effective tool of financial control ? Discuss.
2. Explain the cost concept and the concept of conservation. Why are assets shown at cost even when this market prices far exceeds the cost ? Give reason.
3.Why are Reserves created at the time of preparing the final accounts ? Distinguish
between General Reserve and Specific Reserve and give their examples.
4.Distinguish between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure. what will be the
effect on net profit, if the accountant treats a capital expenditure as revenue expenditure. Discuss.
5. Distinguish between :
(a) Gross Working Capital and Net Working Capital.
b) Current Ratio and Quick Ratio.
c) Direct Labour Rate Variance and Direct. Labour Efficiency Variance.
d) Committed Fixed Costs and Disentionarv Fixed Costs.
6. In what way is financial leverage related to operating leverage ? Discuss with an example.
7. How would you appraise the technical feasibility and financial viabilrty of a project ? Explain.
8.What do you understand by Zero Base Budgeting ? Discuss the steps that are involved in the preparation of Zero Base Budget and describe its advantages over a traditional budget.
9. Explain fully the following statements :
a) very high current ratio is not desirable.
(b) "Cash Budget is a statement of all incomes and expenses during a given period."
(c) "Weighted average cost of capital would always be higher, if the market value weights are used."
(d) Companies with very high profits generally have a low pay out ratio.
10. Following details have been extracted from the annual budget of a manufacturing company for the year 2007 and 2008 :
Particulars Per Unit Rs. Per Annual rs
Selling Price 300
Direct Materials 64
Direct Labor 48
Production overheads:
Variable 32 4000000
Fixed 3000000
Administrative overheads-fixed
Selling and Distribution overheads:
Variable 36
Fixed 20,00,000
Currently the company is operating on a margin of safety of 25%. To improve its
profitability further, the company is considering the following options.
(a) Reduce selling price by 5%. Sales volume is expected to increase by 2A% also fixed production overheads will increase by Rs. 2lakh and fixed selling and distribution over heads by Rs 3 lakh.
b) Increase selling price by 5%. This will cause a drop in sales volume by 10%. To arrest further fall in sales, an increase of Rs 2 lakh will be required under fixed selling and distribution overheads.
c) Production can be increased by 15% by introducing an incentive scheme for labour.
This will be increase direct labour cost by 25%. An additional expenditure of Rs 3lakh would be required under fixed selling and distribution overhead to market the
increased production.
Required :
(a) Current level of production/sales and profit earned.
b) Assuming that (i), (ii) and (iii) above are mutually exclusive and other views remain unchanged, evaluate each of these options.
(c) If the company is able to reduce raw material cost by Rs 5 per unit by making
bulk purchases and reduce the fixed overhead costs by 2 lakh by suitable economy measures, at what selling price per unit should it sell its current production to earn a 10% increase in current profit ?
- The Balance Sheets of ABC Manufacturing Company Ltd. as on December 31, 2007 and 2008 are as follows :
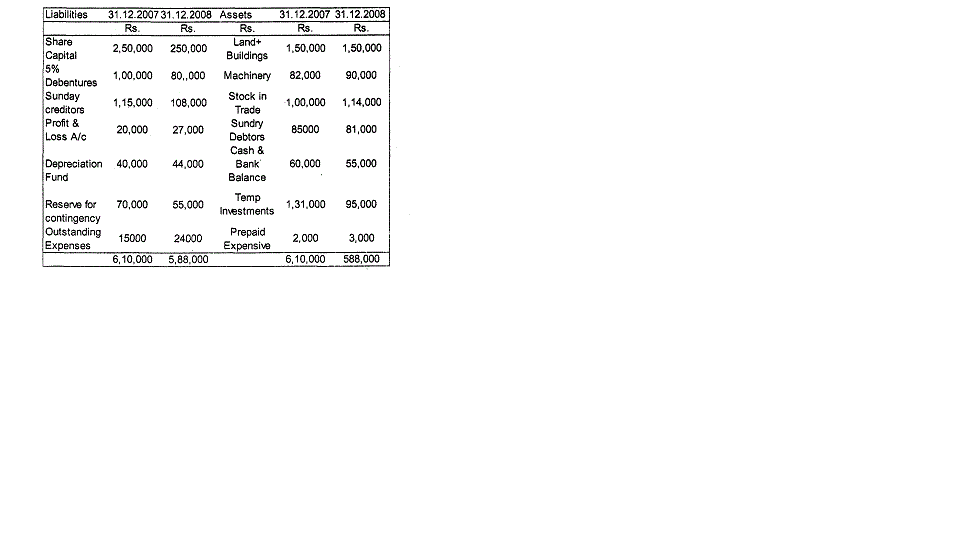
The following additional information is also available.
(a)A new machinery was purchased for Rs. 30,000 and old machinery costing Rs. 15,000 was sold for Rs. 5,000. Accumulated depreciation was Rs. 8,000.
(b) Rs 20,000 5% debentures were reduced by purchase from open market @ Rs 96.
c) Rs 36,000 investments were sold at book value.
d) 12% dividend was paid in cash
e) Rs.15,000 was debited to Contingency Reserve to settlement of previous tax liability.
You are required to prepare :
(a) a statement of changes in Working Capital, and
(b) a statement showing the sources and application of funds.
Ms-4 June 2010
MS-4 june-2010
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
1."In managing cash, the finance manager faces the problem of compromising the conflicting goals of liquidity and profitability". Comment on this statement. How would you determine the optimum cash balance in a business organisation ?
2. What is meant by appropriate capital structure ? Discuss the determinants and features
of an appropriate capital structure for a corporate body.
3. (a) How is a statement of changes in working capital prepared for 'Fund FlowAnalysis' ?
(b) How is 'cash from operating activities' calculated in cash flow analysis ?
4. Write notes on :
a) Going concern.
b) Return on investment.
(c) Management Accounting.
(d) Capital rationing.
5. Explain differences between :
a) Prime cost and factory cost.
b) First in, First out and Last in, First out methods of inventory valuation.
c) Fixed budget and flexible budget.
d) Contribution and margin of safety.
6.Discuss the features of accounting information which can be generated from accounting
records. How do different users use this information ?
7(a) Following information is available for a company for January and February 2009.
January February
Sales (Rs.) 38 lakh 65 lakh
Profits (Rs.) - 3 lakh
Loss (Rs.) 2.4 lakh –
Compute : (i) Break even sales volume
ii) Profit or loss at Rs. 46 lakh sales
iii)Sales to earn a profit of Rs. 5 lakh.
(b) Calculate Direct Material Cost Variances Direct Material usage variance and Direct Material Price Variance from the following information :
Finished production
during the period 1000 units
Opening Stock of material 1000 kg.
Closing Stock of material 2000 kg.
Value of material purchased Rs. 1 lakh
Standard rate of material Rs. 20 per kg.
Standard quantity of material
per unit of finished product 2 kg.
Quantity of material purchased 4000 units
8. From the following information draw up a balance sheet :
Gross profit ratio 20%, liquidity ratio : 1.5
Reserve : Share Capital 0.5 : 1
Networking Capital Rs. 30 Lakh.
Current ratio 2.5, fixed asset turnover ratio : 2 times
Average Debt collection period : 2 months,
Stock turnover ratio : 6 times (cost of sales/closing stock)
Fixed Asset : Shareholders Net worth 1 : 1
Ms-4 June 2011
MS-4 june-2011
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
1. (a) What do you understand by capitalisation of earnings ? How is the value of a firm
ascertained with the help of its earnings ? Explain with an example.
(b) How can accounting reports, prepared on a historical basis after the closure of an accounting period, be useful to mangers in directing the activities of a business ? Discuss.
2. (a) Explain the terms 'Intangible Assets' and 'Contingent Liabilities' giving suitable examples. How are they treated While preparing the Balance Sheet ? Explain with reasons.
(b) what do you understand by the 'net worth' of a company ? how is it different from the
owners' equity ? What items comprise the net worth ? Is dividend policy connected with the net worth in any way ? Explain.
3. Explain the important determinants of the Working Capital needs of a firm. Can two firms with different Working Capital achieve the same amount of sales ? If so, explain how ?
4. Distinguish between :
(a) Profitability index and Profitability Ratios.
(b) Cash Budget and Cash Flow Statement.
(c) Capitalisation of reserves and Capital Reserve.
(d) Depreciation and Amortisation.
5. Explain fully the following statements :
(a) "Where cash flows are uncertain, the principle will be, greater the variability of cash flows, higher should be the minimum cash balance".
(b) 'Companies with very high profits, generally have a low pay out ratio.'
(c) "Debt is double edged knife".
(d) "Lower the Break-even point, better it is."
6. What do you understand by Budgetary Control ? How is it exercised ? What steps should be taken for installing a Budgetary Control system in an organisation ? Discuss.
7. A company produces a single product which is sold by it presently in the domestic market as Rs.75 per unit. The present production and sales is 40,000 units per month representing 50% of the capacity available. The cost data of the product are as follows :
Variable Cost per unit Rs. 50
Fixed Cost per month Rs. 10 lakh
To improve the profitability, the management has three proposals on hand as under :
(a) to accept an export order for 30,000 units per month at a reduced price of Rs.60 per unit, incurring additional variable cost of Rs. 5 per unit towards export packing, duties, etc.
(b) to increase the domestic market sales by selling to a domestic chain stores 30,000 units at Rs. 55 per unit, retaining the existing sales at the existing price;
(c) to reduce the selling price for the increased domestic sales as advised by the Sales
Department as under;
Reduce Sale Price Increase in Sales
per Unit by Expected
Rs. (in units)
5 10,000
8 30,000
11 35,000
Prepare a table to present the results of the above proposals and give your comments and advice on the proposals.
8. The comparative Balance Sheets of ABC Co Ltd. are given below in condensed form.
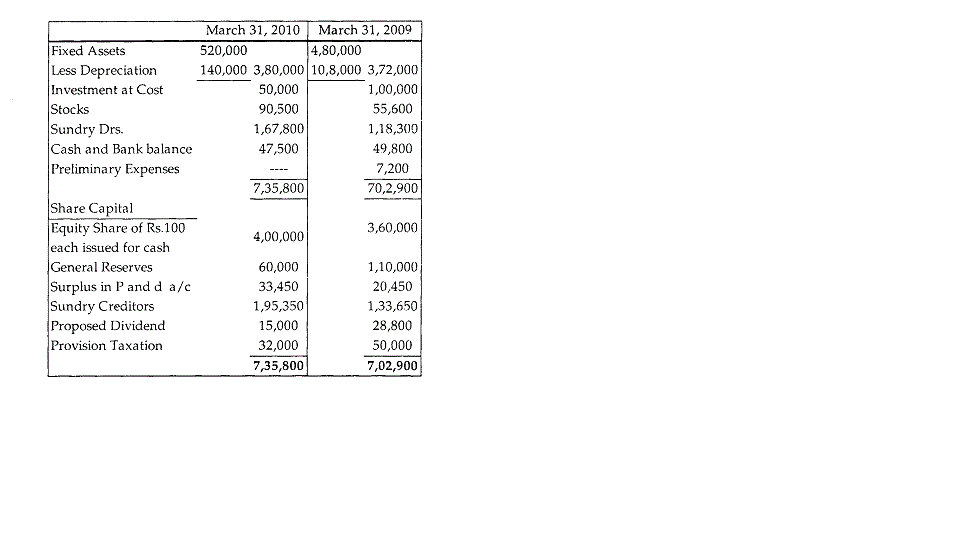
(a) The profit for the year (after providing for depreciation Rs 40,000 writing off preliminary expenses Rs. 7,200 and making provision for taxation Rs. 32,000) amounted to Rs. 38,000.
(b) The company sold during the year old machinery costing Rs. 9,000 for Rs. 3,000.
The accumulated depreciation on this machine was Rs. 8,000.
(c) A portion of the company's investment became worthless and was written off to general reserve. The cost of such investments was Rs. 50,000.
(d) During the year the company paid an interim dividend of Rs. 10,000 and the directors have recommended a final dividend of Rs. 15,000 for the year 2008-09
You are required to :
- (i)prepare a statement of sources
- (ii)and application of funds, and prepare a schedule of working capital changes.
Ms-4 Dec 2007
MS-4 Dec, 2007
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
l. (a) What dq you understand by Accounting Standards ? How do they differ from Accounting Concepts ? Why should the accounting practices be standardised ?
(b) Why are the fixed assets shown at their book value rather than their market value, even if the latter has appreciated significantly ? Give reasons.
2. (a) How would Explain the you compute the cost of goods sold ? Explain two methods of inventory valuation
(b) What is depreciation and what is the rationale behind making a provision for depreciation in the process of matchlng income and expenses ?
3. What do you understand by Zero Base Budgeting ? How does a Zero Base Budget differ from a Flexible Budget ? Discuss the steps involved in Zero Base Budgeting.
4. Distinguish between :
(a) Accounting Rate of Return and Internal Rate of Return
(b) Profitability Index and Profitability Ratios
(c) Bonus Shares and Rights Shares
(d) Earnings yield and Dividend yield
5. A manufacturing company produces and sells products P; Q and R. It has an available machine hour capacity of one lakh hours, interchangeable among the 'three products. Presently the company produces and sells 20,000 units of P and 15,000 units each of Q and R. The unit Selling Price of the three products P, Q and R is Rs. 25, Rs. 32 and Rs. 42 respectively. With this price structure and the aforesaid sales-mix, the company is incurring loss. The total expenditure exclusive of fixed charjes (presently Rs. 5 per unit) is Rs. 13.75 lakhs. The'unit cost ratio amongst the three products P, Q and R is 4 : 6 : 7.
Since the company desires to improve its profitability without changing its cost and price structures, it has been considering-the following three mixes so as to be
Within its total available capacity :
|
Products Mix1 Mix 2 Mix 3 |
|
P 25000 20000 30000 Q 15000 12000 5000 R 10000 1 8000 15000 |
You are required to compute the quantum of loss now incurred and advise the most profitable mix which could be considered by the company.
6. Comment upon the following statements giving appropriate reasons :
(a) Higher net profit margin higher rate of return on investments
(b) EBIT-EPS analysis is an the capital structure. need not necessarily lead to
investment. important tool for designing the capital structure
(c) Cost of retained earnings is lower than the cost of equity.
(d) Many reasons account for direct material variances
- "The conventional break-even analysis is based on a number of assumptions." Explain and illustrate the concept of break-even analysis and justify the above statement.
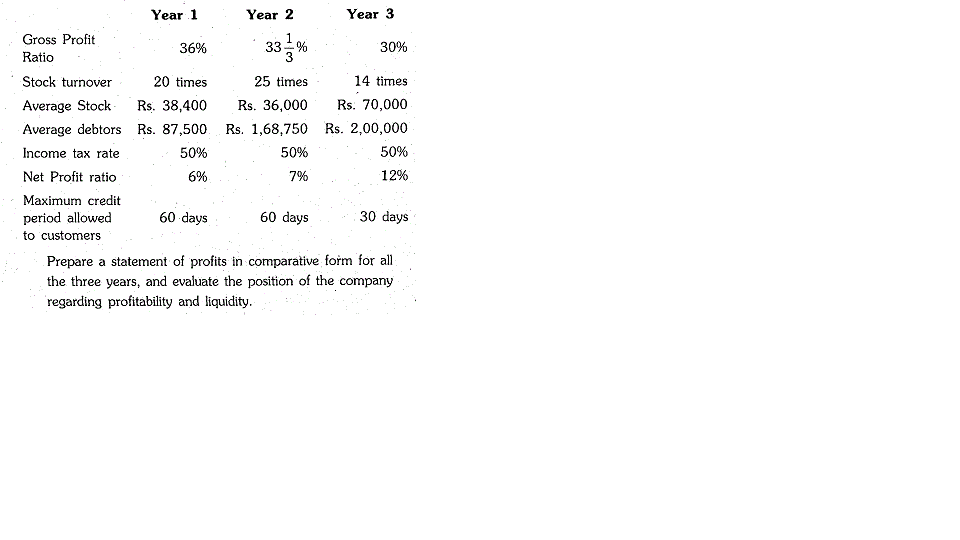
8. The following three years information is available ior XYZ Ltd. for
MS-4 DEC 2008
MS-4 Dec, 2008
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
l. (a) Explain the Money Measurement Concept and the Accrual Concept. What are the limitations of the former concept. Explain.
(b) What do you understand by Accounting Standards ? Why are they necessary ? Explain with examples.
2. (a) Explain First-In First-Out and Last-In First-Out Methods of Inventory Valuation. In an inflationary situation, which method will give higher valuation of the inventory, other things remaining the same ? Explain.
(b) what do you understand by Capitalisation of earnings ? How is the value of a firm ascertained with the help of its earnings. Explain with an example
3. what do you understand by Composite Cost of Capital ? How is it computed ? Explain with an example. How would you support the statement that debt becomes more expensive after a certain point is reached ? Explain.
4. Distinguish between
(a) Preference Shares and Bonus Shares.
(b) Earnings Yield and Dividend Yield.
(c) Sales Price Variance and Sales Volume Variance.
(d) Shut Down Costs and Sunk Costs.
5. The summarised result of the operations of a company for the first year of its existence is glven below:
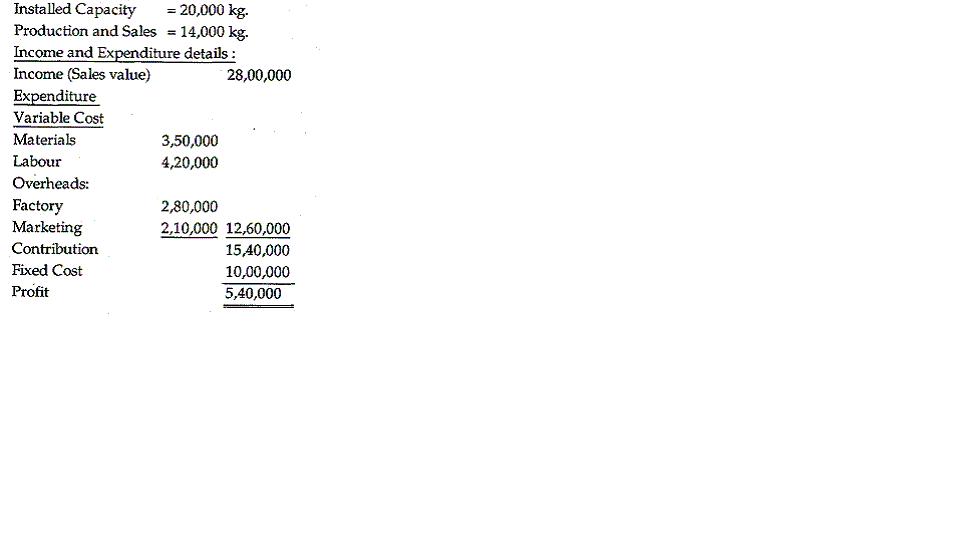
6.What is meant by Net Present Value ? Why is Profitability Index considered useful ? Discuss the Iimitations of Investment Appraisal Techniques.
7.Explain fully the following statements :
(a) Higher profit margins need not necessarily lead to higher rate of return on investement.
(b) Actual performance can be compared with the budget performance with the help of three ratios.
(c) A high operating leverage is not always desirable.
(d) Dividend, Investment and Financing decisions are inter-dependent