
Ignou Question Bank (432)
Ignou Question Bank from previous year papers
Children categories

Ms-495, Question Bank (2)
Ms-495, Question Bank, Ethics And Corporate Governance In Banks

IB0-04 Question Bank (3)
IB0-04 Quesiton Bank, Export - Import Procedures And Documentation

MC0-03 Question Bank (2)
MC0-03 Question Bank, Research Methodology And Statistical Analysis
Ms-10 june 2011
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-10 june, 2011
MS-10 : ORGANISATIONAL DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND CHANGE
1. Identify the key factors which affect the Organisational Design ? Briefly discuss the principles of a good Organisational Design. Explain with examples.
2. Distinguish between the Functional and Product Organisation, and Line and Staff Organisation. Discuss their merits and demerits with suitable examples.
3. What is Organising and Analysing Work ? Briefly discuss 'Scientific Management' and 'Human Relations' approaches to organising and analysing
work.
4. Define and describe Organisational Diagnosis and its purpose. Discuss with suitable examples the role of various organisational sub-systems and processes as components of organisational diagnosis.
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Institution Building.
(b) Questionnaire as a diagnostic tool.
(c) Essentials for success of Organisational Development.
(d) Team Building.
(e) Commonly used interventions for managing change.
"Sunrise" is the brand name of Sunrise Industries Ltd., a leading industrial house`of northern India with an annual turnover of more than Rs. 450 crores. The company produces a wide variety of electrical home appliances which are popular not only in India, but in foreign countries also. The Board of Directors is headed by Mr. Kamaldeep and its executive director is Mr. Ankit. The company has its head office at New Delhi and works at Ludhiana, about 300 km. from New Delhi. It is in the process of starting a new factory at NOIDA (about 25 km. from New Delhi) for the manufacture of refrigerators and air-conditioners. Sunrise Industries wasn`t always a big industrial giant. In fact, it had a very humble beginning. Kamaldeep, an electrical engineer, set up a small scale industrial unit in 1975. To start with, he undertook assembly and sale of sewing machines under the name `Sunrise` and gradually started manufacture of certain spare parts. Because of better quality,,greater selling skills and lower profit margin, his sales turnover touched the figure of Rs. 1 crore during 1979-80. The products included sewing machines, irons, fans, geysers, etc.
In 1981, Kamaldeep entered into a partnership with Ankit, an M.B.A., who contributed a lot of capital into the business. The firm acquired a big industrial plot in the New Industrial Area of Ludhiana and converted their business into a company known as Sunrise Industries Ltd. in 1982. The brand name `Sunrise` was also registered in the name of the company. The company started the commercial production of single tub washing machines and instant geysers in 1983. Kamaldeep looked after production and Ankit took care of marketing and finance. They never looked back as they had a motivated work force of 40 workers and 5 foremen who worked like a big family.
It was during 1990 that the company shifted its head office to New Delhi and entered into a technical collaboration agreement with a foreign company. As a result, new generation twin tub semi-automatic washing machines and vacuum cleaners were launched in 1991 and the products were well received in the market because of latest technology and expanding market for electrical gadgets. The sales turnover increased tremendously every year.
QUESTION
1. What changes in structural dimensions have taken place in Sunrise Industries ?
2. Is the present structure organic ? Give reasons for your answer.
3. Which approach to organisation do you feel can help the company tackle the current problems ?
Ms-10 Dec 2007
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-10 Dec, 2007
MS-10 : ORGANISATIONAL DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND CHANGE
1.Describe the meaning and characteristics of an organisation. DisCuss Mintzberg's theory and its relevance in the existing business scenario.
2. what are the objectives and issues involved in quality of work life ? Describe the aspects which have to be included in quality of work life programme in the modern organizational context.
3. Describe various roles and competencies required for an effective change agent. Explain with examples.
4. Describe any two OD interventions and their advantages and disadvantages, citing examples from organizational context.
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Observation Method as a diagnostic tool
(b) Scientific Management
(c) Matrix Organisation
(d) Bureaucratic Model of Organisational Design
(e) Business Process Re-engineering
6. Read the following case carefully and answer the questions given at the end :
Since 1994, Boeing began the process of remaking the company for the next round of aircraft purchases. Every part of the company is involved, from engineering to manufacturing. The focus of the change is that Boeing is a manufacturing company rather than an engineering and technology company. Due to changes in the air travel business, the major commercial airlines are demanding lower airplane prices and significantly lower operating costs. Airbus continues to be a f.ierce competitor, so Boeing must meet the competition early and on every front. (Boeing bought McDonnell Douglas in 1 997.)
It is not as if the company is in financial trouble. Its new .model 777 is generating lots of orders. plans are in the works for a new supersonic and another jumbo jet for commercial sales, and several new project possibilities exist for the defence division. The new 777 was designed completely on the computer so that designs went straight from the designers' computers to the machine tools for manufacturing. It can carry as many as four hundred passengers, fifty more than the comparable Airbus 33 t.
It is 15 per cent more fuel efficient, and can fly over eight thousand miles non-stop. orders are coming in faster than for any other new plane, although its price is pretty steep , $12 -$15 million, depending on interior layout.
Boeing's new CEO, Philip Condit, must continue the reductions in cycle time and cost cutting, started by his predecessor, Frank Shrontz, because airlines are making
their purchase decisions differently than in the past, even choosing in some cases. to refurbish older planes rather than buy expensive new ones. The changes started with Condit and his team of presidents of the divisions of commercial planes, defence and space, and computer services. This group differs notably from its predecessors in that they have met together for several years to discuss the good and bad things about each other's divisions and the future of the company. They all embrace the new togetherness theme as the primary means through which the company will be able to reduce cycle times, improve delivery times, cut product development time, and reduce total costs. In the former structure the design and manufacturing groups were separate. Design and engineering groups would design the planes and then give ihe plans to manufacturing to build. When problems existed in the design, they would be sent through the hierarchy back to engineering for correction. Under the new structure, comprehensive design-and build teams include members of all groups involved. Therefore, planes are originally designed to meet customers' needs, are easier to build, and corrections are made faster. For example, previously, when tool builder Tony Russell had a problem with an engineering design or specification, he would have to go to his supervisor and the problem would be shuffled through to engineering. Now he goes directly to the engineering and design group, gets the problem solved, and gets back to work with the correct design. This type of revision in the process has helped reduce the product delivery time from eighteen to ten months. The team approach and working-together ideas were used extensively on the 777. Some teams included tool makers, designers, manufacturing workers, suppliers, and even customer representatives. Contrary to past procedures, workers on the line were allowed to change how planes were built, which has significantly decreased costs. Condit has instituted 350 degree performance reviews in which managers are evaluated by their subordinates, their peers, and their own supervisors to improve understanding of how they are doing from all perspectives. Employee empowerment is increasing at all levels. Condit and his team are having quite an impact throughout the company.
Questions
(a) The new way of organizing at Boeing most resembles which of the classical types of organizing ?
(b) How have responsibility and authority been altered under Condit's new approach ?
(c) Describe the new ways of organizing ai Boeing in terms of the configurational and operational aspects of structure
Ms-10 Dec 2008
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-10 Dec, 2008
MS-10 : ORGANISATIONAL DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND CHANGE
1. What are the key factors which affect Organization Design, examples ?
describe briefly with examples
2. Identify the main considerations in preparing a questionnaire and collecting data ? Describe the dimensions which can be diagnosed through questionnaire, citing suitable examples.
3. Describe diagnostic workshop methodology ? Discuss the conditions under which the workshop methodology can be used, with suitable examples.
4. Enumerate various significant competencies required by a change agent. Discuss cognitive and inter-personal competencies, with examples.
5.Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Quality of work life.
(b) Management Assessment Centres
(c) Mintzberg's Typology.
(d) Factors influencing Institution Building.
(e) Organisational Effectiveness.
6. Please read the case and answer the question given at the end.
Mr. Anand occupies No. 2 position in the Corporate Planning Department of multi-product company having a tumover of more than Rs. 900 crores and operating in a high technology (hi-tech) industry. For the last five years, Anand has been associated with strategic planning of the company and recently he has been deputed to a task force to reorganise the company to cope up with the changing technology and environment. At the last meeting of the Board of Directors of the company, the members expressed their concern about the falling competitive position of the company in the industry. The main reason
cited bv the Cheif Executive was the outdated organisation structure which has not undergone any change for the 10 years,though the size, technology and environment of the company have changed tremendously. It was on the advice of Chief Executive that the Bord of Directors decided to set up a task force for the company's reorganisation..
At the first meeting of the task force, Anand, who is an expert in planning, convinced the other members to adopt the following procedure :
(i) Determine exactly what type of structure the company has at present.
(ii) Determine the type of environment the company faces now and the weaknesses of the present structure
(iii) Forecast the environmental changes in the future and the type of technology to be used by the company.
(iv) Design the organisation structure to meet the future challenges
It was discovered that the company is currently structured along classical lines and the company is operating in a highly dynamic environment. The environment in future is likely to be more uncertain because of fast changes in technology and requirements of customers and competition by MNCs. The task force came to the
conclusion that the structural design must be responsive to change and if this is not done, the company's survival in the market would be made more difficult.
Questions :
(a) How far do you agree with the procedure adopted by the task force ?
(b) Explain how the system and contingency approches can contribute to the analysis of this case.
(c) What type of organisation designshould the task force reconunend ? Explain its broad features.
Ms-10 Dec 2009
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-10 Dec, 2009
MS-10 : ORGANISATIONAL DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND CHANGE
1. Describe recent trends in work organisations and their effect on employees.
2. Discuss the factors affecting organisational design and their relevance with suitable examples.
3. Describe any two OD interventions and their advantages.
4. Describe and explain the importance of interview as a diagnostic tool.
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
a) Competencies of change agents
b) Job Rotation and Job Enrichment
c) Inverted Pyramid
d) Work shop Methodology as a diagnostic tool
(e) Managing Resistance to change
6. Read the following case carefully and answer the questions given at the end.
The middle managers of a large firm were told by the corporate human resources office that a group of consultants would be calling on them later in the week. The purpose of the consultants' visit would be to analyze interfunctional relations throughout the firm. The consultants had been very effective in using an OD intervention called team building. Their particular approach used six steps. When their approach was explained to the managers, a great deal of tension was relieved.
They had initially thought that team building was a lot of hocus-pocus, like sensitivity training, where people attack each other and let out their aggressions by heaping abuse on those they dislike. By the same token, these managers generally felt that perhaps the consultants were not needed. One of them put it this way : "Now that we understand what is involved in team building, we can go ahead and conduct the sessions ourselves. All we have to do is to choose a manager who is liked by everyone and put him or her in the role of the change agent/consultant. After all, you really don't need a high priced consultant to do this team-building stuff. You just have to have a good feel for human nature." The
other managers generally agreed. However, the corporate human resources director turned down their suggestion. He hired the OD consultants to do the team building.
Questions :
a) Bring out the main features of this case.
b) What is a team building approach to organization development ? Do you think the managers had an accurate view of this OD technique ?
c) Do you think that the managers had an accurate view of the role of external consultants ?
d) What will be your plan of action in the situation ?
Ms-10 Dec 2010
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-10 Dec, 2010
MS-10 : ORGANISATIONAL DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND CHANGE
Ms-10 Dec 2011
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.com
MS-10 Dec, 2011
MS-10 : ORGANISATIONAL DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND CHANGE
1. Discuss the meaning and characteristics of an organisation. Briefly discuss various approaches to understanding organisations.
2. Describe the evolutionary process of organisational design. Briefly discuss the contingency model of organisation design, with suitable example.
3. Define and discuss the elements of designing a job. Briefly describe the impact of technology on Job Design. Explain with suitable examples.
4. Define Organisational Development and briefly describe various stages of Organisational Development, with suitable examples.
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Impact of information Technology on organising work
(b) Quality of work life
(c) Methods of Organisational Analysis
(d) Survey Feedback
(e) Resistance to change.
6. Please read the case and answer the questions given at the end.
Tidewater Manufacturing Company is a medium-size producer of machine gaskets operating in the south - eastern part of Bombay. Until about two years ago, the company's financial outlook was very strong. Recently, however, it has been facing much stiffer competition from foreign producers and a variety of internal problems have also begun to surface.
Top management believes that they know how to deal with the external issues. But nothing they do will be successful -until the existing problems with employees have been addressed. Unfortunately, there is no clear consensus among the top management about the real nature or extent of employee concerns. Tandon, the firm's President, has decided that a management committee should be formed to look into the increasing absenteeism and turnover rates, grievances, and generally weak morale. Turnover, for example, has been running at a rate of 72 per cent for the past year, grievances are up by about 25 per cent, and two recent attitude surveys showed that in some departments employee morale is, in fact, down. Tandon considers the firm to be an enlightened employer that cares about its employees. The committee he has appointed includes himself, Rajesh, Head of Marketing, Umesh, Plant Manager in-charge of production, and Deepak, Personnel Director. The committee is now meeting in formal session.
Tandon : I appreciate your taking time to be here today. As you know, several employee-related issues have been slowing us down of late, and given the stiff competition we are getting, I believe it is high time we find out what is going on. Rajesh, how about if you lead off ?
Rajesh : As I see it, we have not been able to make the production changes we talked about last year because of all this hassling with employees. I have been giving the problem some thought and I believe that we need to light a fire under those people down the line. My sales people are out there beating the bushes, but they cannot sell a product that just does not measure up. Last week, one of my people lost a major sale to that new West German firm.
Umesh : I agree with some of what you are saying Rajesh, but I would not lay all the blame on the production crew. After all, we have been losing a lot of good people lately and it takes time to train the new hands. Besides that, I cannot seem to get anybody to come to work on Friday. If I make any moves, the union representative hits me with a pile of grievances for unnecessary harassment. If you have some answers, I am sure we can make the modifications you were just talking about.
Tandon : I guess we know where you two stand, but I would still like another opinion. Deepak, how do you see things ?
Deepak : My reaction is that we probably cannot deal with issues internally. I would suggest that we bring someone in from the outside to diagnose the situation. 1 have been doing some study and I think that some of the problems of turnover and absenteeism plus the poor showing in the recent attitude survey my office administered, might be due to discontent with our production line approach. Some of those people have been doing the same thing, day in and day out, for years. They are probably bored stiff. Maybe it is time for us to consider something like job redesign.
Tandon : Okay, but all I remember about job redesign was something about job enrichment ten years ago in one of my MBA courses. Frankly, I have not kept up and I would not even know where to begin.
Rajesh : Would we not be better off if we just started a new incentive programme ?
Umesh : Incentives could work, but I would like to follow up on Deepak's idea. By the way where does the union fit into all of this ?
Deepak : Let me do some checking and see if I can get a line on a good consultant. It should take me about ten days to put together the information we need.
Tandon : Well, let us leave it at that and plan to meet again a week from Thursday. At that point , the meeting adjourned with the understanding that the firm would consider some form of job redesign.
Questions :
(a) You are a consultant called into this situation. How would you proceed ? Would job redesign be of use here and, if so, how ?
(b) What alternative approaches to job redesign might this firm consider, i.e., would job
enlargement be better than job enrichment, would a team concept be appropriate ?
(c) Should the top management involve the union at this stage ? What should it tell the employees ?
Ms-9 june 2009
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 June , 2009
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. a) Explain in brief the opportunity cost principle. Give examples in support of your answer.
b) What is a Production Possibility Curve (PPC) ? Explain how it reflects the opportunity cost principle.
2. Explain briefly the following give examples :
a) Expert opinion
b) Surveys
c) Market experiments
3.One of the decision problems that concerns aproduction process Manager is, which input combination to use'. Keeping this in mind explain with the help of examples, what is the optimal combination of inputs ? You may use the ISO cost
isoquant framework in your answer.
4.Market selection process includes firms entry, then its survival and finally the exit process'. Critically examine the statement in view of barriers to entry with suitable examples from the sector of your choice.
5.Write short notes on any four of the following :
a) Peak Load Pricing
b) Law of Demand
c) Oligopoly
d) Objective of the firm
e) Economies of scope
f) Accounting and Economic Costs.
6. a) Suppose that a linear demand function is given as :
Q=100-5P
Calculate the price elasticity of linear demand function given when P =10 and
when P =8. Also find the slope of the demand curve.
b) .Explain the concept of break-even analysis with the help of examples. What strategic decisions can a manages take on break-even analysis ?
c) What are the limitations of break-even analysis ? Explain .
Ms-9 june 2007
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 June , 2007
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1.Differentiate between 5 types of rnarket using the following characteristics :
(a) Number of independent sellers
b) seller concentration
c) Product differentiation
(d) Conditions of entry
2.Describe the various types of price discrimination. Is price discrimination a characteristic of monopoly or perfect competition ? Explain.
3. (a) Explain and illustrate the various returns to scale.
(b) What is Operating Leverage ? Give examples.
4. Discuss various Demand Forecasting Techniques. Illustrate your answer with examples.
5. Write notes on any four of the following :
(a) Value maximisation
(b) Technical efficiency
(c) Peak load pricing
(d) Equilibrium price
(e) Price bundling
6. Fill in the blanks :
(i) If e > 1, the total revenue curve has a _____slope.
(ii) The value of total revenue reaches _________when elasticity is equal to 1.
(iii) If the demand is _______ do increase in price will result in a decrease of the total revenue.
(iv) Any straight line supply curve passing through the _______ has elasticity equal to one.
Ms-9 june 2008
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 June , 2008
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. Explain why the average cost curve is U-shaped. The long run average cost curve is always an envelope of short run average cost curves. Discuss.
2. Explain the equilibrium of a firm by using the marginal cost and marginal revenue curves. Why is the firm under perfect competition described as a price taker ?
3. Explain break-even analysis on the basis of its concept, use, drawbacks and advantages.
4. Write notes on the following :
(a) Discounting principle
(b) The Equi-marginal principle
5. Distinguish between the following :
(a) Economies of scale and Economies of scope
(b) Demand curve and Demand schedule
6 . Choose the correct answer.
(i) The responsiveness or sensitivity of a firm's profits to changes in output is measured by a firm's
(a) operating leverage
(b) contribution margin
(c) degree of operating leverage
(d) returns to scale
(ii) The contribution margin per unit is equal to the
(a) price'of a good
(b) difference between total revenue and total cost
(c) difference between price and average total cost
(d) difference between price and average variable cost ,
(iii) Which type of market structure does not typically
have a negatively-sloped market demand curve ?
(a) Monopoly
(b) Perfect competition
(c) Oligopoly
(d) all of the above typically have negatively-stoped market demand curves
(iv) The restaurant industry has a market structure that comes closest to
(a) Monopolistic competition
(b) Oligopoly
(c) Perfect competition
(d) Monopoly
(v) If marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, increasing output would
(a) reduce profits
(b) increase profits
(c) have no impact on profits
(d) reduce the rate of growth in profits
8. Read the following text and answer the questions that follow :
THEORY AND REAL WORLD MARKETS
The theory of perfect competition describes how firms act in a market structure where (1) there are many buyers and sellers, none of which is large in relation to
total sales or purchases; (21 sellers sell a homogeneous product; (3) buyers and sellers have all relevant information; (a) there is easy entry and exit. These assumptions are closely met in very few real world markets. These assumptions may however be approximated in some real' world markets. In such markets, the number of sellers may not be large enough for every firm to be a price taker, but the firm's control over price may be negligible. The amount of control may be so negligible, in fact, that the firm acts as if it were a perfectly competitive firm.
Similarly, buyers may not have all relevant information concerning price and quality, but they may still have a great deal of information and the information
they do not have may not matter. The products that the firms in the industry sell may not be homogeneous, but the differences may be inconsequential. In short, a market that does not meet the assumptions of perfect competition may nonetheless approximate those assumptions to such a degree that it
behaves as if it were a perfectly competitive market. If so, the theory of perfect competition can be used to predict the market's behaviour.
Questions ;
(a) A price taker does not have the ability to control the price of the product it sells. What does this mean ?
(b) Why is a perfectly competitive firm a price taker ?
(c) The horizontal demand curve for the perfectly competitive firm signifies that it cannot sell any of its products for a price higher than the market equilibrium price. Why can't it ?
(d) Suppose the firms in a real world market do not sell a homogeneous product. Does it necessarily follow that the market is not perfectly competitive ?
Ms-9 june 2010
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 June , 2010
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. (a) Discuss the Laws of Returns to scale and describe the three stages of returns to
scale.
(b) Explain why Marginal Product (MP) is greater than (less than) Average Product
(AP) when AP is rising (falling).
2. Write notes on any four :
a) Tastes and preferences as determinants of demand.
b) Economies of scale.
(c) Breakeven output level.
d) Equimarginal principle.
e) Kinked demand curve.
3. Explain the concept of law of demand. What causes the market demand curve for a commodity to increase (shifting up) and decrease (shifting down) ? Explain.
4. Write five important characteristics of monopoly. Establish the profit maximising output of a monopoly firm.
5. (a) Discuss the relationship between marginal cost, average cost and total cost.
(b) Explain Profit Maximization under cartel condition. Plot necessary graph.
6. State True or False and justify. Attempt any five :
a) The demand for a commodity is inversely related to price of its substitutes.
b) When income increase, the demand for essential goods increases more than proportionately.
c) Decrease in input prices causes a leftward shift in supply curve.
d) In the long run, there are no variable costs.
e) Retail trade is an example of monopolistic competition.
f) The profit will be maximum where MC = MR in general.
g) In a firm's short-run production function, the firms labour and plant are held
constant while its machinery is allowed to vary.
h) The Law of Diminishing returns is unrealistic because it implies that we could
feed the world from our kitchen garden.
i) Even if there are many buyers, imperfect competition can exist in a market.
j) A monopolist will never produce at the elastic portion of the demand curve.
7. Explain decision under risk. Describe strategic decisions based on decision tree.
MS-9 June , 2009
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. a) Explain in brief the opportunity cost principle. Give examples in support of your answer.
b) What is a Production Possibility Curve (PPC) ? Explain how it reflects the opportunity cost principle.
2. Explain briefly the following give examples :
a) Expert opinion
b) Surveys
c) Market experiments
3.One of the decision problems that concerns aproduction process Manager is, which input combination to use'. Keeping this in mind explain with the help of examples, what is the optimal combination of inputs ? You may use the ISO cost
isoquant framework in your answer.
4.Market selection process includes firms entry, then its survival and finally the exit process'. Critically examine the statement in view of barriers to entry with suitable examples from the sector of your choice.
5.Write short notes on any four of the following :
a) Peak Load Pricing
b) Law of Demand
c) Oligopoly
d) Objective of the firm
e) Economies of scope
f) Accounting and Economic Costs.
6. a) Suppose that a linear demand function is given as :
Q=100-5P
Calculate the price elasticity of linear demand function given when P =10 and
when P =8. Also find the slope of the demand curve.
b) .Explain the concept of break-even analysis with the help of examples. What strategic decisions can a manages take on break-even analysis ?
c) What are the limitations of break-even analysis ? Explain .
More...
Ms-9 june 2011
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 June , 2011
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. "The opportunity cost of anything is the return that can be had from the next best
alternative use". Elucidate the statement with reference to the opportunity cost principle
applied in agricultural sector.
2.The demand function is written as Qd= F (Po, Pc, Ps, Yd, T, A, CR, R, E, N, 0) Describe each of this variables separately giving examples.
3. What do you understand by 'Price discrimination' and the various types of price discrimination ? I-low is the optimal quantity to be supplied in different markets determined ? Elucidate your answer with suitable examples.
4. Write short notes on the following :
(a) Kinked demand curve.
(b) Time Series Analysis of Demand Forecasting.
5. Define elasticity of demand. How are the price, income, cross elasticities measured ?
Explain their role in business decisions.
6. Read the following case and answer the questions given at the end.
TAKE THE BULL BY THE HORN
Through its relatively brief history, the Reliance group has specialised in taking gambles, sometimes huge ones. A pattern repeated time and again - such as when it set up capacities for Polyester Staple Fibre (PSF) which was the same size as the domestic market or when it put up a 27 million tonne refinery in Jamnagar, which is close to a third of India's demand for petroleum products.
There's no gamble quite so audacious as the one that's underway. The Rs. 25,000 crore Reliance Infocom project that's currently taking shape aims at no less than a complete remake of India's telecom landscape to emerge as India's number one telecommunications company, ahead of the state-owned behemoth Bharat Sanchar Nigam l td.
It's also an attempt to realign Reliance's revenues and profits - which today originate entirely from manufacturing - with India's economic profile, in which services account for over 40 per cent of GDP. "Reliance's revenues will have to become diversified with
a larger proportion originating from services which would be in keeping with the changing structure of India's economy," says Mukesh Ambani, vice chairman of Reliance
Industries. Rs. 8000 crore will be invested over a three - year period. As of now, it's full steam ahead for Reliance's Infocom plans. As it had done earlier in oil and gas. Reliance plans to emerge as an integrated player, focusing on the entire range of telecom services
ranging from high - speed internet access for business and consumers, call centres, data centres, cellular phone services and domestic and international long distance telephony. Apart from the gamut of telecom services, Reliance's integration plans are in one respect unique in the telecom industry. If senior group officials are to be believed, the company has plans to assemble cellular phones and set-top boxes.
At the core of the Infocom project is a 115,000 km fibre optic backbone covering 115 cities across 12 States, accounting for over 50 per of India's GDP. The company plans to become what the industry jargon refers to as a carriers' carrier, where it hires out infrastructure to other telecom operations. Here Reliance, along with the Bharti group, has obtained a licence for providing domestic long-distance services. In fact, these are the only two companies to do so. The total domestic long-distance market is worth Rs. 6,000 crore. Of this, the market available to the long distance operator is likely to be Rs. 2,400 crore, according to a December 2000 Merrill Lynch report. This is based on a 30 : 40 : 30 revenue share between the originator, the carrier and the last-mile access provider. However, Reliance would hope for a larger share since it plans to fill all the three roles. Merrill Lynch estimates that the domestic long-distance revenues accruing to the carrier would amount to Rs. 2760 crore in 2002 - 03, of which Reliance is expected to garner 20 per cent - or Rs. 620 crore.
As part of its plans to enter international long-distance telecommunication, Reliance has already submitted an expression of interest for international long-distance operator VSNL. The total international long-distance market in India right now is Rs. 4,900 crore.
Reliance's own estimates for revenue and profitability have not been made publicly available. However, internal estimates reportedly project revenues of Rs. 30,000 crore, which is roughly a third of the total telecommunication market of around Rs. 1,00,000 crore estimated for fiscal year 2004 - 05. The annual total telecommunications market is around Rs. 42,000 crore. These estimates are of course based on the assumptions of a rapid take-off in traffic, particularly data traffic. Check out some figures: out of the 30 million households that have an income over Rs. 4000, an estimated 20 million are in the urban market and 10 million in the rural market. Out of the urban people, 13 million already have fixed-line connections. And out of the 10 million rural customers, 6.5 million already have fixed lines.
In the light of the above: "what kind of growth can one really expect" for the telecommunication sector in India as such and Reliance lnfocom in particular ?
Questions :
(a) Is there such a market in India for all the huge plans that they have ?
(b) Can you support it as a case of economies of scope ?
(c) Does it not lend to monopolistic conditions ? Give reasons.
Ms-9 Dec 2007
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 Dec, 2007
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. What is the basic objective of a firm ? Distinguish between 'Accounting Profit and 'Economic Profit' with the help of an illustration.
2. What do you understand by demand forecasting while describing the regression method of demand forecasting explain why it is important for the firm to forecast demand
3. Distinguish between the following with the help of illustrations :
(a) Fixed costs and Variable costs
(b) Short'run costs and Long-run costs
(c) Direct costs and Indirect costs
(d) Total cost, Average cost and Marginal cost
4. (a) Differentiate between Monopoly and Monopolistic competition giving examples
(b) Explain why profit is maximum at a level where MC = MR. Is profit always maximum when MC =MR ? Comment.
5. (a) What are the different types of statistical analyses used in the estimation of production function ? Explain briefly with the help of examples. Discuss the limitations of different types of statistical analysis.
(b) Briefly explain how the Cobb Douglas production function can be used to determine returns to scale.
6. (a) Which of the following commodities has most inelastic demand ? Give reasohs for your answer.
(i) Soap
(ii) Salt
(iii) Penicillin
(iv) Ice-cream
(v) Cigarettes
(b) Suppose the demand function of a product is given as
Q =500 - 5P. Find the profit maximising price when
i) MC:=0
ii) MC=20
7. Suppose you are a sales manager of an organization. Explain how does the analysis of demand contribute to business decision making, in the light of the responsibilities of a sales manager.
Ms-9 Dec 2008
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 Dec, 2008
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. Explain the concept of price elasticity of demand and the relationship between price elasticity, total revenue and marginal revenue
2. Show graphical derivation of MP and AP curves from the total product function. Show also the three stages of production. What economic purpose do the stages
of production serve ?
3. Explain with examples economies and diseconomies of scale. How do economies and diseconomies of scale determine the shape of the LAC ?
4. Write notes on the following :
(a) The Equi Marginal Principle
(b) Elasticity of Substitution
(c) Linear Cost function
(d) Types of markets
5. (a) Under perfect competition average revenue equals average cost in the long run. Why do firms produce under such a condition ?
(b) A monopolist earns super normal profits even in the long run. Discuss
6. (a) Write True or False :
(i) In a firm's short-run production function, the firm's labour and plant are held
constant while its machinery is allowed to vary.
(ii) The law of diminishing returns is unrealistic because it implies that we could feed the world from our back garden.
(iii) The least-cost input combination producing a given level of output always be achieved in the short run.
(iv) The law of eventually diminishing returns describes a short run situation in which labour varies but fixed factors do not.
(v) The greater the cost of storing a good, the greater will be the gap in its price now and 2 years later.
(vi) Scale is a short-run concept.
(vii) When an input's average product exceeds its marginal product, average product is increasing.
(viii) The long-run average cost curve slopes downward over a range of output where a firm experiences a decreasing returns to scale.
(ix) Because consumers like variety, we cannot conclude that monopolistic competition is inefficient.
(x) The theory of the kinked demand curve does not predict the price where the kink will occur.
(b) The market demand function for a product sold by a monopolist is given below :
QD=2500-10P
The monopolist marginal cost function is :
MC=10+Q
Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity
Case study IBM
7. Read the following case and answer the questions given at the end.
LONG-RUN COSTS AT IBM
(LONG RUN COST FUNCTION)
The IBM Corporation is a leading manufacturer of electronic computers. Based on its internal memoranda, IBM's long-run total cost of producing various quantities of its Pisces (370/168) machines was as shown below :
For output levels in the relevant range, the equation
for this total cost function is
C = 28,303,800 + 460,800 Q,
where C is total cost (in dollars) and Q is the number of machines.
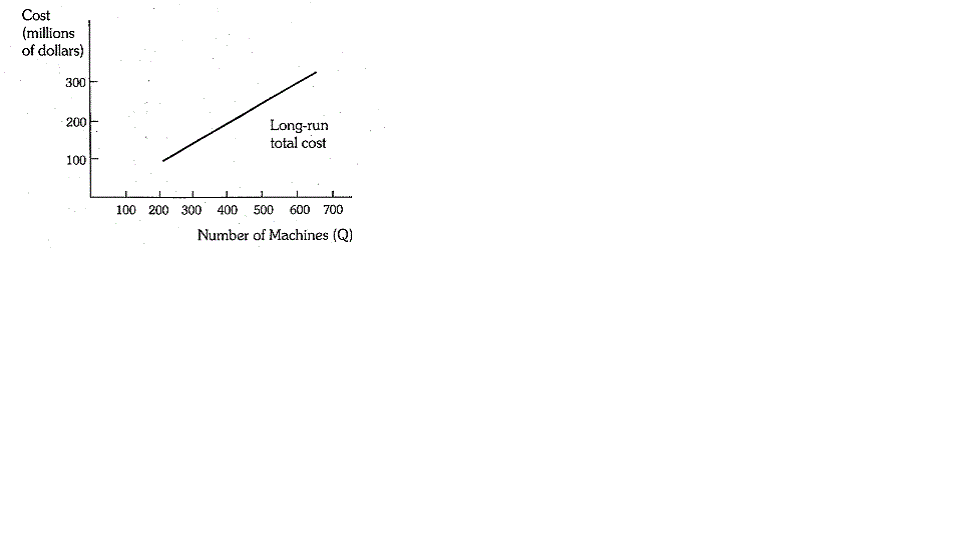
A) If the entire market for this type of machine is 1,000 machines, and if all firms have the same long-run total cost function, to what extent would a firm with 50 percent of the market have a cost advantage over a firm with 20 percent of the market ?
b) What is the long-run marginal cost of producing such a machine ? Does marginal cost depend on output ?
c) Do there appear to be economies of scale ?
d) The data presented above are forecasts of costs based largely on engineering data, not on historical record of actual costs. Why would IBM make such forecasts ? What factors might result in errors in these forecasts ?
Ms-9 Dec 2009
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 Dec, 2009
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. Distinguish between profit maximisation and value maximisation giving examples.
2 (a) Briefly explain the concept of price elasticity of demand giving suitable examples.
(b) What are the determinants of price elasticity ? Explain giving examples.
3. Write short notes on the following giving suitable examples :
a) Breakeven output level
b) Profit contribution analysis
(c) Operating leverage
4. Critically comment on the factors which determine the nature of competition giving suitable examples.
5 (a) Why will managers prefer to operate in a cartel type environment as opposed to
competition ? Explain.
(b) Sustaining collusion is difficult for firms. Explain why, with reference to the prisoners dilemma.
6.You are given to understand that the existing firm in a market drives 80% of its revenues from 20% of its customers. Your boss wants you to develop a strategy to enter this market to compete with the existing firm (incumbent). Your answer should focus on :
a)How you would target existing customers ?
b) How you would seek to attract new customers ?
c) It is possible that the incumbent will also change his strategy following your decision
to enter. How according to you will the incumbent react ?
d) What will be your counter strategy to combat the incumbent ?
7. What do you understand by 'laws of production ? Explain the production function with one variable input highlighting the law of diminishing marginal returns and the stages of production
